Understanding & Creating a Bill of Supply for your Business

Another crucial document in the GST-compliant tax system is a bill of supply. Some registered organizations are prohibited from including GST on tax invoices they issue. The reason for this is that, in accordance with Section 10 of the CGST Act of 2017, they are either providing goods or services that are exempt from the GST or are otherwise unable to charge clients GST.
As a result, such enterprises must issue a Bill of Supply instead of a Tax Invoice under GST. In this post, we'll go over what it is, who can issue one, what it contains, and how to structure one.
Definition of Bill of Supply for Businesses
A Bill of Supply is a document prepared by a seller to a buyer when the seller cannot impose GST or the nature of the transaction does not trigger GST. This indicates that there is no tax included in a bill of supply.
However, subject to certain criteria, if the value of the supply is less than Rs. 200, a Bill of Supply is not necessary to be generated.
According to section 31(3) of the CGST Act, 2017, a registered taxable person must issue a Bill of Supply instead of a tax invoice when providing GST-exempt goods or services or when paying lesser tax under the Composition Scheme as per section 10 of the Act.
Similar to the Tax Invoice, this bill serves as a record of the sale made by the registered taxpayer and includes information such as the nature and cost of the supply.
However, a tax invoice is generated whenever a registered taxpayer provides goods or services for which the GST is applicable, and this tax information is included in the tax invoice. In contrast, a Bill of Supply is generated when the registered supplier supplies the recipient with products or services for which GST is not applicable.
When is a bill of supply required?
If products or services having a value of more than Rs. 200 are supplied, an invoice or a bill of supply must be produced in accordance with GST. If GST is not applicable to the transaction, it is issued by the supplier in place of an invoice. For additional reference, the following lists some situations in which providing a bill of supply rather than a GST invoice is appropriate.
- Supplier is not GST Registered
The ability to collect GST from customers or make an input tax credit claim is not available to entities that are not registered under the GST. Therefore, non-registered firms having a turnover of less than Rs. 20 lakhs in the majority of states or Rs. 10 lakhs in states that fall under a special category may issue a bill of supply to the consumer without mentioning the CGST, SGST, IGST, and GST Compensation Cess component.
- Distributor of Exempt Supplies
Instead of issuing a tax invoice, a bill of supply should be submitted if a GST-registered business only deals in exempted supplies.
- Composition Scheme Vendors
A compounding dealer, registered under the GST composition scheme is restricted from collecting tax or claiming input tax credit and is only permitted to provide bills of supply. Furthermore, the terms "composition taxable person, not eligible to collect tax on supplies" must appear at the top of the bill of supply issued by a party registered under the composition scheme.
- Exporters
GST does not apply to a recipient who is a foreign national and exports are zero-rated under this tax. As a result, when it comes to exports, the exporter can exclude the CGST, SGST, IGST, and Cess from the bill of supplies. Similar to a composition scheme dealer's bill of export, an exporter's bill of supply must include the following information:
“Supply Meant For Export On Payment Of IGST” (If IGST has been paid)
“Supply Meant For Export Under Bond Or Letter Of Undertaking Without Payment Of IGST” (If IGST is not paid)
The Difference between a Tax Invoice and a Bill of Supply
For all sorts of taxable sales, whether they are localized or centralized, a Tax Invoice is used, but a Bill of Supply is used for all types of exempt sales or sales made by Composition Dealers.
While CGST, SGST, and IGST should all be listed individually on a tax invoice, no taxes should be mentioned on a bill of supply.
In the case of an unauthorised buyer, name, address, state, and place of delivery are mandatory if the invoice value before taxes exceeds. However, a Bill of Supply is exempt from this requirement. As long as it includes all the mandatory information required by the GST Invoice Rules, the provider is free to create the Bill of Supply format.
Understanding the components of a bill of supply
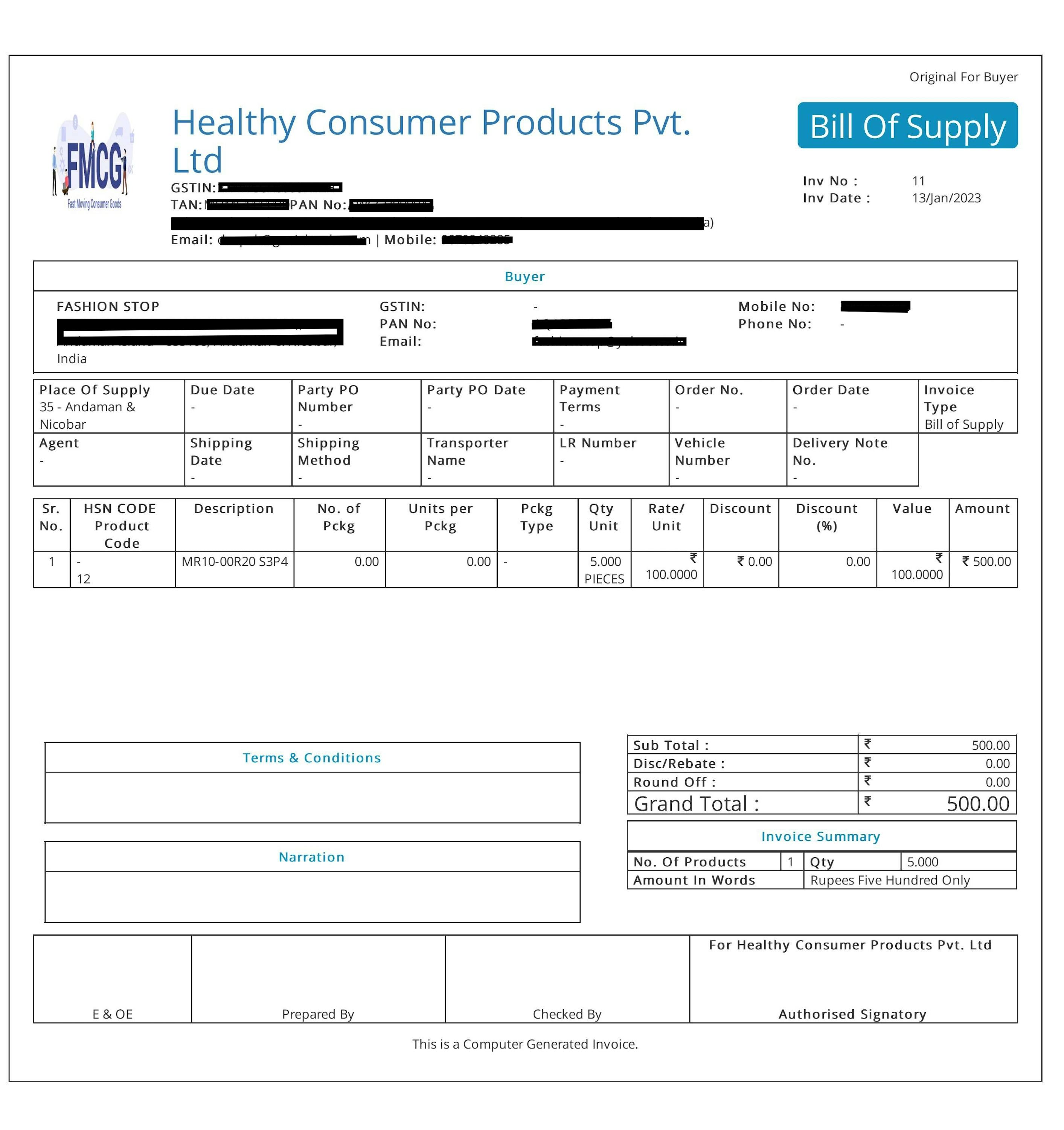
These key points must be included in the bill of supply:
(a) The supplier's name, address, and GSTIN;
(b) A serial number with a maximum of 16 characters, in one or more multiple series, unique for each financial year, made consisting of letters, numerals, the special characters "-" and "/," or any combination thereof.
(c) The date the bill was issued;
(d) The recipient's name, address, GSTIN (if registered under GST), or UIN;
OR
Those who receive supplies worth more than Rs. 50,000 must provide their name, address, and source of supply (if they are not GST-registered);
e) HSN Code for goods or SAC for services (restricted to companies with annual revenues of more than Rs. 1.5 crores);
f) Detailed product or service descriptions, or both;
(g) The value of the supply of goods or services, or both, after deducting any applicable discounts or abatements;
(h) The supplier's physical or digital signature, or that of his duly authorised agent.
How to issue a bill of supply
To create a bill of supply under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India, you will need to follow these steps:
1. Acquiring the required data:
You will need specific data on hand in order to prepare a bill of supply. This comprises:
- The supplier's name and GSTIN (GST identification number): This is the company or person that is selling the products or offering the services. The type of bill generated depends on the taxpayer's attributes or type. If the person has chosen composition rather than being a regular registered person for GST, a bill of supply is sent instead of a tax invoice. In a related manner, GST does not impose any tax obligations on those who are not registered.
- The recipient information, including name and address: This is the individual or company making the purchase of the goods or services.
- The nature, quantity, and cost of the goods or services being provided: You must give a thorough explanation of what is being sold, the number of each good or service being sold, and the overall cost of the transaction. Every taxpayer should be able to tell the difference between taxable and non-taxable things. If the products being traded are taxable products, a tax invoice rather than a bill of supply must be raised. However, a bill of supply is required when the products are non-taxable. Flour, sugar, bread, milk, and other items are a few examples of nontaxable products.
2. Using an accounting or invoicing software:
You can create a bill of supply that complies with GST standards using a number of software tools that are readily available. GenieBooks 100% cloud accounting software lets you enter the necessary data and creates a bill of supply automatically.
3. Entering required information
Once you've chosen an accounting software, you'll need to enter the necessary information into the application. This information consists of the supplier's name and GSTIN, the recipient's name and address, and the kind, quantity, and cost of the goods or services being provided.
4. Calculating the GST amount
Include a statement that the supplies are not taxable: A bill of supply is used in place of a tax invoice for supplies that are not taxable. Therefore, you should include a statement on the bill of supply indicating that the supplies are not subject to tax. Based on the data you submitted, the software determines this sum automatically. Once the bill has been provided, the taxpayer is required to keep a copy in their possession as well as to upload the necessary information to GSTR 1 for the applicable month.
5. Printing or saving the bill
You can print or save the bill after you have submitted all the necessary data. Ensure that the recipient receives a copy of it.
It's crucial to remember that a bill of supply is only necessary under specific conditions, such as when the supplier is ineligible to collect GST or when the goods or services being provided are not taxable.